Dandruff is a common chronic scalp condition, which is marked by itching and flaking of the skin on your scalp. Although dandruff isn't contagious and is rarely serious, it can be embarrassing and sometimes difficult to treat.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain, but often occurs without any symptoms.
Dehydration occurs when you lose more fluid than you take in, and your body doesn't have enough water and other fluids to carry out its normal functions. If you don't replenish lost fluids, you may suffer serious consequences.
Delirium is a serious disturbance in a person's mental abilities that results in a decreased awareness of one's environment and confused thinking. The onset of delirium is usually sudden, often within hours or a few days.
Dementia is a general term for a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life. Memory loss is an example. Alzheimer's is the most common type of dementia. About dementia. Diagnosis.
Often thought of as just a symptom, depression is itself a medical condition and can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems.
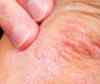
Dermatitis is a general term that describes an inflammation of the skin. There are different types of dermatitis, including seborrheic dermatitis and atopic dermatitis (eczema). Although the disorder can have many causes and occur in many forms, it usually involves swollen, reddened and itchy skin.
Diabetes mellitus is an umbrella term that describes a group of conditions where the body's ability to control and use glucose (blood sugar) is altered.
High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) affects people who have diabetes. Several factors can contribute to hyperglycemia, including food and physical activity choices, illness, or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication.
Low blood sugar (diabetic hypoglycemia) affects people who have diabetes. It occurs when there's too much insulin and not enough sugar (glucose) in your blood. Several factors can cause diabetic hypoglycemia, including taking too much insulin or diabetes medication or skipping a meal.
Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy.
Type 1 diabetes in children is a condition in which your child's pancreas no longer produces the insulin your child needs to survive, and you'll need to replace the missing insulin using shots or an insulin pump.
Type 2 diabetes, once known as adult-onset or noninsulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose), your body's main source of fuel.
Type 2 diabetes in children is a chronic condition that affects the way your child's body metabolizes sugar (glucose).
Diabetes mellitus is an umbrella term that describes a group of conditions where the body's ability to control and use glucose (blood sugar) is altered.
When you hear the term "diabetes insipidus," you may assume it's related to what's commonly known as "sugar" diabetes, or diabetes mellitus. While the disorders share a name and have some common signs, in fact diabetes mellitus (type 1 and type 2) and diabetes insipidus are unrelated.
A diabetic coma is a life-threatening diabetes complication that causes unconsciousness. If you have diabetes, dangerously high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) or dangerously low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can lead to a diabetic coma.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when your body produces very high levels of blood acids called ketones. Diabetic ketoacidosis develops when you have too little insulin in your body.
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar can injure nerve fibers throughout your body, but diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in your legs and feet.
Diabetic Retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that results from damage to the blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (retina). At first, diabetic retinopathy may cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems.