-
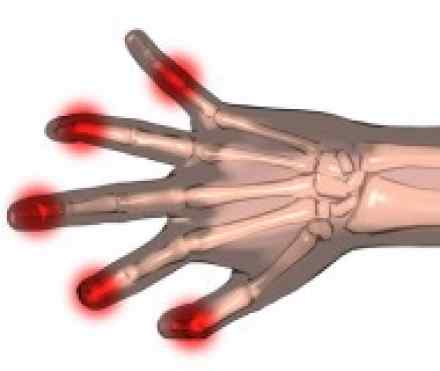
Intense joint pain. Gout usually affects the large joint of your big toe, but it can occur in your feet, ankles, knees, hands and wrists. The pain is likely to be most severe within the first 12 to 24 hours after it begins.
-
Lingering discomfort. After the most severe pain subsides, some joint discomfort may last from a few days to a few weeks. Later attacks are likely to last longer and affect more joints.
-
Inflammation and redness. The affected joint or joints become swollen, tender and red.
Causes
Gout occurs when urate crystals accumulate around your joint, causing the inflammation and intense pain of a gout attack. Urate crystals can form when you have high levels of uric acid in your blood. Your body produces uric acid when it breaks down purines — substances that are found naturally in your body — as well as in certain foods, such as organ meats, anchovies, herring, asparagus and mushrooms.
Normally, uric acid dissolves in your blood and passes through your kidneys into your urine. But sometimes your body either produces too much uric acid or your kidneys excrete too little uric acid. When this happens, uric acid can build up, forming sharp, needle-like urate crystals in a joint or surrounding tissue that cause pain, inflammation and swelling.
How do you treat it?
Like any disease, even if there is no cure, there is almost always something you can do to manage it and take control. There are three main areas involved in the treatment of any disease:
For information on medicines and therapies relevant to Gout, make an appointment at Lynch's Pharmacy, Broadale, Douglas, Cork on 021-4366923.
Learn all about the drugs used to treat the disease and any complementary medicines or therapies proven to help. Equip yourself with the tools to manage the condition and not be managed by it.
How do you live with it?
Certain adjustments may be needed to get on with your life, and often, some simple tips and advice can go a long way to making these changes.
When you come to a Lynch's Pharmacy Clinic, we give you all the necessary information available to make your life more manageable and allow you to better live with your condition.
References
Gout-http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gout
Gout, a comprehensive overview, http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/gout/DS00090